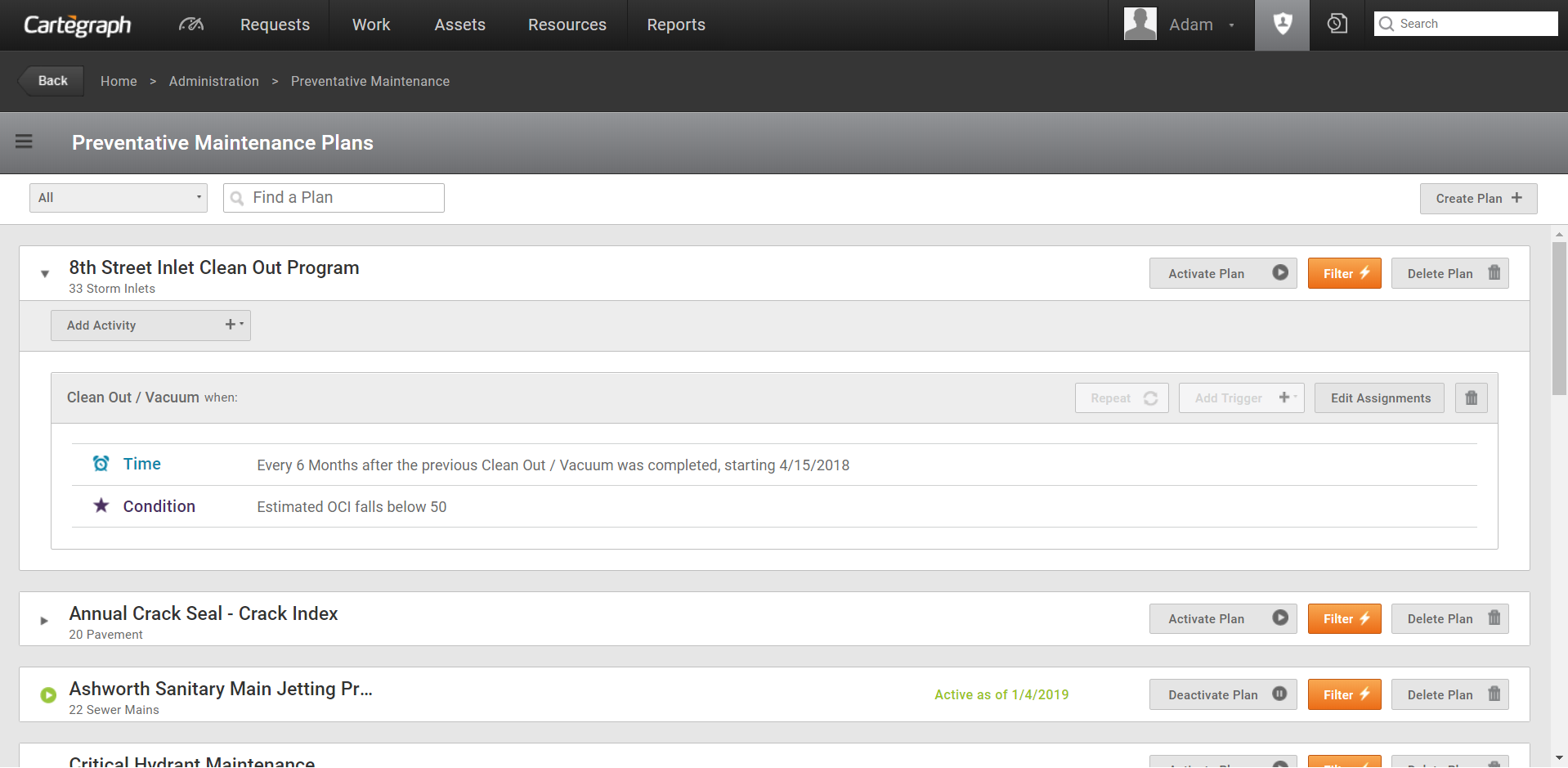
Preventative Maintenance plans are used to prolong the service life of assets through proactive maintenance. Use this functionality to set conditional and/or chronological triggers that, when activated, automatically create the necessary follow-up tasks. The ability to create Preventative Maintenance plans is limited to Cartegraph Administrators only. Here’s what you need to know:
Preventative Maintenance has four parts:
- Plans are a collection of assets you want to maintain. Plans contain Schedules.
- Schedules are the Activities or work that create proactive tasks. Schedules contain Triggers.
- Triggers are the rules governing when to fire the scheduled Tasks (work).
- Labor Assignments define who the scheduled Task is assigned to.
The Administrator determines which tasks can be created by a Preventative Maintenance Plan, how often those tasks can be created, and the triggers that set the task creation process in motion. Triggers are what the system looks for to create a task for the asset.
There are four trigger types:
Condition: Create Tasks based on the condition of an asset. For example, a water hydrants OCI falls below 75, inspect it. The Preventative Maintenance engine compares the current condition of an asset to the value you set in the Plan’s Condition based Trigger. When the current condition falls at or below your set value a Task with the plan’s Activity is created for that asset. To prevent duplicate tasks, condition-based plans always follow the After Complete rule: Do not create tasks if an open Task for the same asset and activity already exists.
Time: Create Tasks after some amount of time has passed. For example, repaint water hydrants every two years. The Preventative Maintenance engine looks at the last time the plan’s maintenance activity was completed and creates the tasks when the user-specified time interval has passed. For example, the time interval of two years does not start until the current Repaint task is completed. Similar to condition triggers, time Triggers follow the After Complete rule.
Repeat: This is a type of time trigger and is different from the time trigger:
- Does not follow the After Complete Rule so you could end up with more than one open task to do the same thing for the same asset
- Does not base the interval on the completion of a task. It starts as soon as the interval ends
- For example, Storm Outlets are required by the EPA to be inspected twice a year or every 6 months. If you schedule the first inspection task for June 1 and don’t complete that task until August 1, the next task is remains scheduled for Dec. 1
Usage: Available for only Equipment Preventative Maintenance plans. Cartegraph recommends always combing usage and time triggers for equipment plans. This is because without a time trigger a piece of equipment could miss the usage trigger and needs the fallback of the time trigger, similar to oil changes for vehicles.
User Interface
- Analytics Dashboard
- Navigation Persistence
- Global Search
- Table of Contents/ Layers
- Map Tools
- Documents Attachments
- List View Data Export
- More Information…
Request Management
Work Management
- Work Orders
- Repeating Work Orders
- Tasks
- Activities
- Task Calendar
- Time Sheets
- Distribute Resources
- Task Triggers
- Preventative Maintenance
- More Information…
Asset Management & Analytics
Resource & Inventory Management
Report Management
Mobile Management
- Cartegraph for iPad and Cartegraph One Feature Comparison
- Cartegraph for iPad
- Cartegraph One
- More Information…
Workflow Management
System Management
- Structure Manager
- Library Manager
- Layout Manager
- Esri and Active Directory
- Security Role Administration
- System Licensing
- System Requirements
- More Information…
