Asset Condition Manager allows users to create, update, delete, duplicate, and maintain Prediction Groups, Condition Groups, and Condition Categories.
Condition Categories
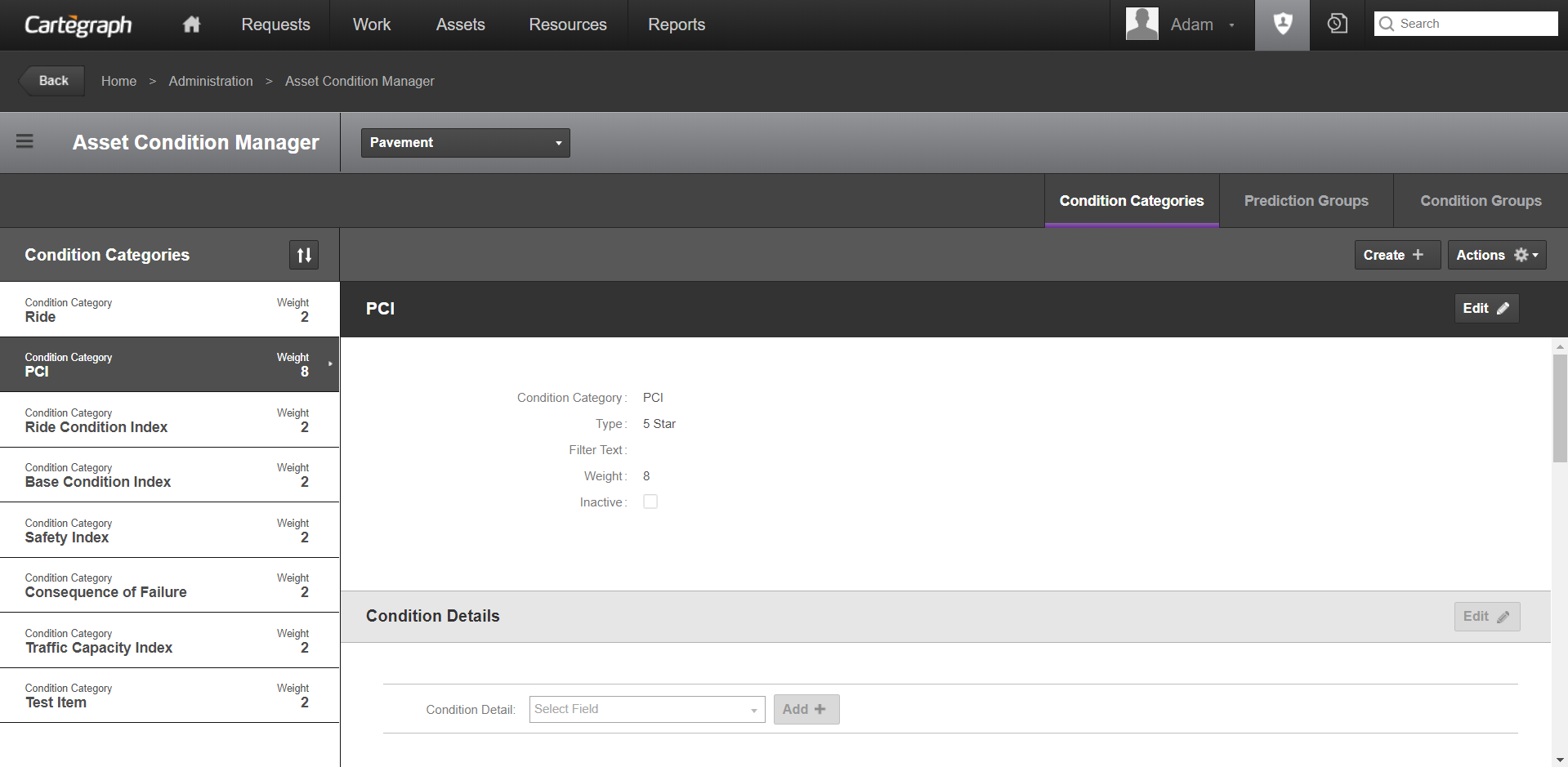
Condition categories are characteristics observed during inspections and can be used to estimate asset deterioration. The weight indicates the impact of a condition category on the asset’s Overall Condition Index (OCI).
- Create Condition Categories if your organization inspects for characteristics not found in the start up data.
- Change Condition Category weights if your organization places more or less emphasis on a particular condition when assessing OCI.
- The Legend Ra and Background Ra Condition Categories for Signs as well as the PCI Condition Category for Pavement and Pavement Area cannot be deleted.
- The filter text lets you filter the assets the Condition Category applies to at a finer level. You cannot enter anything in the Filter Text field. This field displays the results of the advanced filter you create. For example, the Pavement Condition Category, Safety, should only apply to pavement records with four or more lanes. Click and create the filter “Number of lanes is greater than 3” for this Condition Category.
- Impacts is a child recordset available for condition categories for Sign Assets.
- Index Mappings is a read-only child recordset to condition categories.
- Examples of condition categories that come with start up data are Aesthetics, Surface and Structure.
You must have an advanced feature extension for these additional benefits:
- The Type determines how the condition category will be measured during an inspection.
- Each Condition Category must have a performance curve, to accurately calculate an asset’s remaining life.
- If you do not collect Sign Ra readings, do not set performance curves for Legend Ra and Background Ra Condition Categories.
- Impacts and Index Mappings are child recordsets available to all condition categories.
- Impacts and Index Mappings are edited in Asset Condition Manager.
Prediction Groups
You must have administrator rights to access this feature.
- Prediction Groups allows a user to maintain asset performance curves.
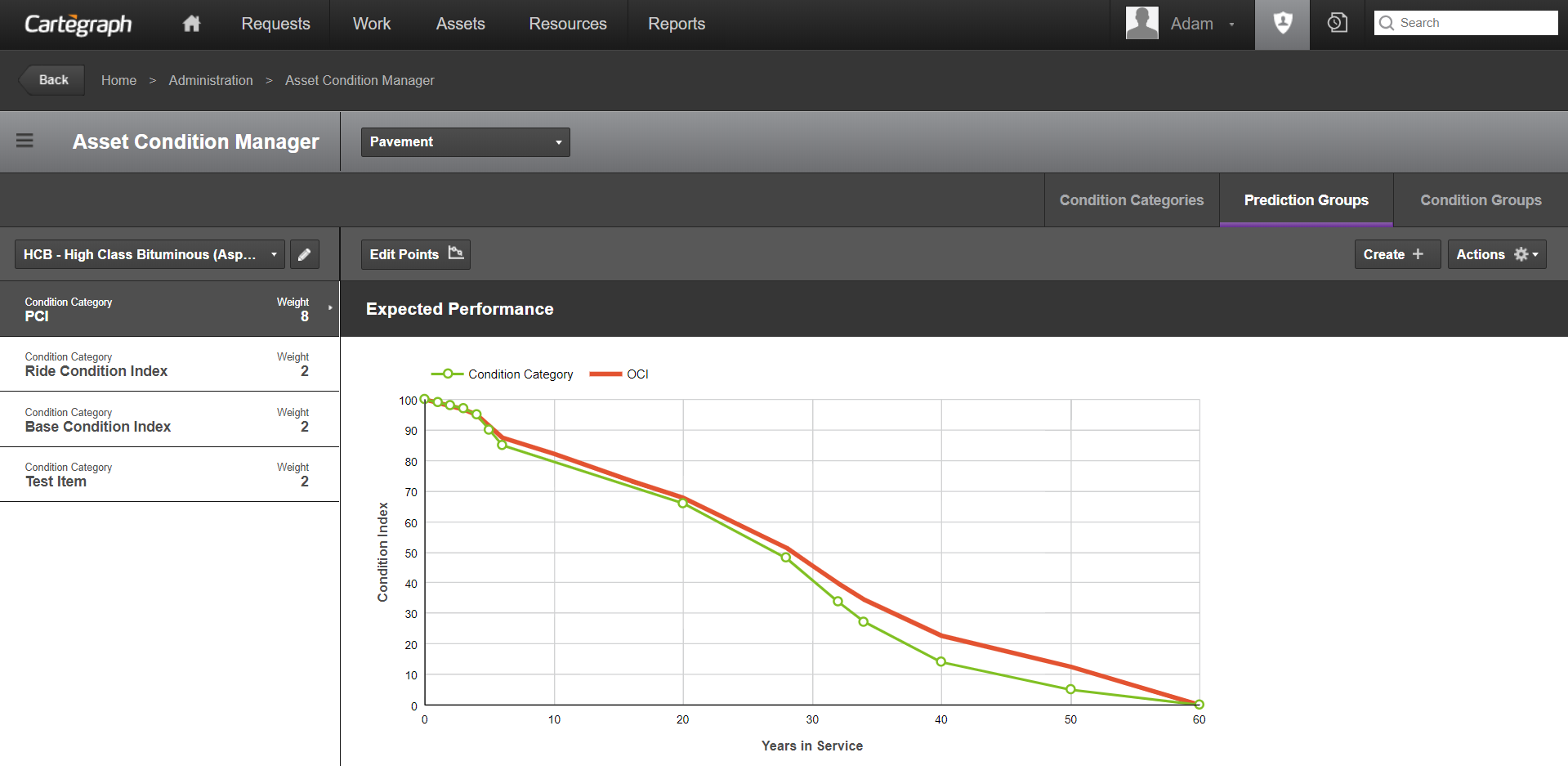
- Performance curves track asset deterioration for individual condition categories over time.
- The deterioration data is stored in prediction groups. You assign an asset to a prediction group based on the filter.
- The filter text lets you define the group of assets a Prediction Group applies to. You cannot enter anything in the Filter Text field. This field displays the results of the advanced filter you create. For example, pipes made of the same type of material, such as concrete, deteriorate at a similar rate. Create a Water Main prediction group named Concrete Mains. Click Filter and create the filter “Material is equal to Concrete”.
- The performance curve is graphed using Years in Service (the asset’s age) and Condition Index (the asset’s condition value).
- The performance curves reflect the anticipated deterioration of each Condition Category, and as a result of the Overall Condition Index, if no maintenance is done to that asset. The weights assigned to each Condition Category help determine the OCI curve. Year values should begin at 0 and end at the asset’s anticipated expiration age. Index values typically begin at 100 and always end at 0. Each curve must have at least two points.
- When you set up performance curves, each condition category curve is combined, through a weighted average, to generate the Overall Condition Index (OCI) curve. The points of the OCI curve cannot be directly accessed or edited. The OCI curve is automatically updated based on edits to the condition category curves.
- You can click on the performance curve’s Legend to hide and show the corresponding curve:
Condition Groups
This functionality is found in the Cartegraph Administration>Asset Condition Manager.
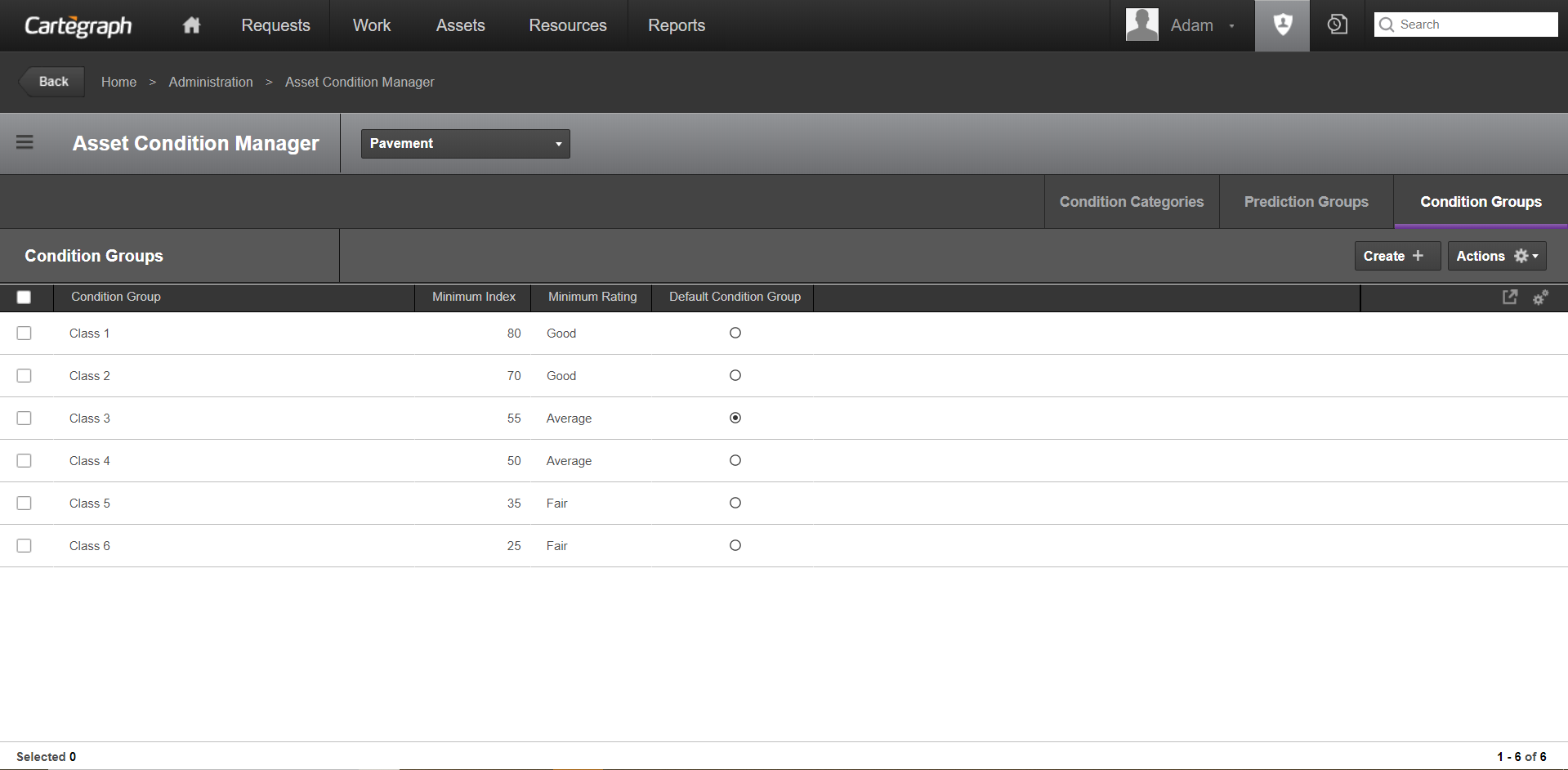
- A Condition Group establishes the point an asset is considered below the minimum acceptable condition or failure point. Assign an asset to a condition group based on the filter.
- When an asset reaches its minimum condition, it is considered to have no remaining life. The Act Before field displays the date an asset’s OCI goes below the minimum index as defined by the asset’s assigned Condition Group.
- The Minimum Index is the lowest point at which the condition is deemed acceptable. If the index calculation results in a value lower than this, the condition is unacceptable.
- Minimum Rating identifies the rating of the minimum index.
- The filter text lets you define the group of assets a Condition Group applies to. You cannot enter anything in the Filter Text field. This field displays the results of the advanced filter you create. For example, roadways with the same functional classification may have the same minimum acceptable condition. Create a Pavement condition group named Rural Arterial. Click Filter and create the filter Functional Classification is equal to Rural Arterial.
Condition Category Measured Value
Measured Value is a field on the Condition Category recordset under an asset’s Inspection recordset. It represents the inspected value for each condition category. When a star is selected during an inspection, the system looks at the index mappings for that condition category to determine the Index for that inspected condition category. The measured value is the number of stars (0-5) that represents the condition of the asset for that condition category.
With the Advanced Assets Extension, when a measured value is selected/entered during an inspection, the system looks at the index mappings for that condition category to determine the Index for that inspected condition category.
The value of the Measured Value field depends on the condition category type:
5 Star
- The measured value is the number of stars (0-5) that represents the condition of the asset for that condition category.
Index
- The measured value is the number entered (0-100) that represents the condition of the asset for that condition category.
- There are no index mappings for this Type, so the measured value sets the Index with the same number.
Number
- The measured value can be any positive or negative number that falls within the bounds of the Index Mappings for the condition category.
- If the number is not specifically mapped in the Index Mappings but falls within the bounds, the system uses the existing index mappings and interpolates an Index.
Quantity
- The measured value can be any positive or negative amount including a unit, that falls within the bounds of the Index Mappings for the condition category.
- The unit can be the default or a convertible unit. If a convertible unit is selected, the system converts it to the default unit to determine the Index based on the Index Mappings, however the selected unit is saved on the Inspection.
- If the number is not specifically mapped in the Index Mappings but falls within the bounds, the system uses the existing index mappings and interpolates an Index.
- An example of a Quantity type condition category where the Unit Category is Temperature and the Default Unit is C for Celsius, but the inspection is recorded in Fahrenheit:
- All Index Mappings are created as Celsius.
- During the inspection, the measured value is set to 77 F. The system converts this measured value to 25 C to determine the inspected Index based on the Index Mappings.
Option
- The measured value can only be one of the Index Mapping values.
If there are no Index Mappings for a Condition Category that requires them, a warning indicator displays in edit mode of the Inspection.
User Interface
- Analytics Dashboard
- Navigation Persistence
- Global Search
- Table of Contents/ Layers
- Map Tools
- Documents Attachments
- List View Data Export
- More Information…
Request Management
Work Management
- Work Orders
- Repeating Work Orders
- Tasks
- Activities
- Task Calendar
- Time Sheets
- Distribute Resources
- Task Triggers
- Preventative Maintenance
- More Information…
Asset Management & Analytics
Resource & Inventory Management
Report Management
Mobile Management
- Cartegraph for iPad and Cartegraph One Feature Comparison
- Cartegraph for iPad
- Cartegraph One
- More Information…
Workflow Management
System Management
- Structure Manager
- Library Manager
- Layout Manager
- Esri and Active Directory
- Security Role Administration
- System Licensing
- System Requirements
- More Information…
